Dans les dernières semaines, j’ai vu passé deux articles s’interrogeant sur les quantités d’oxygène que l’on délivre aux patients. Le premier est une étude danoise sur la quantité d’oxygène administrée (FiO2) pendant une anesthésie générale et le second est un article d’analyse de la littérature de deux auteurs britanniques sur les méfaits potentiels de l’oxygénothérapie « libérale » en réanimation .
Pourquoi administrer plus d’oxygène que nécessaire à un patient pendant une anesthésie ? L’idée peut paraitre d’autant plus paradoxale que la consommation d’oxygène baisse pendant une anesthésie générale. En fait il y a deux concepts qui ont conduit à ça : la prévention des nausées-vomissements post-opératoires (NVPO) et la prévention des infections du site opératoire (surtout les abcès de paroi en chirurgie viscérale). Une méta-analyse sur la prévention des NVPO par de haut débit d’oxygène semble aujourd’hui écarter cette intervention . La prévention des infections de paroi par l’oxygène semblait par contre possible d’après une méta-analyse publiée en 2009 .
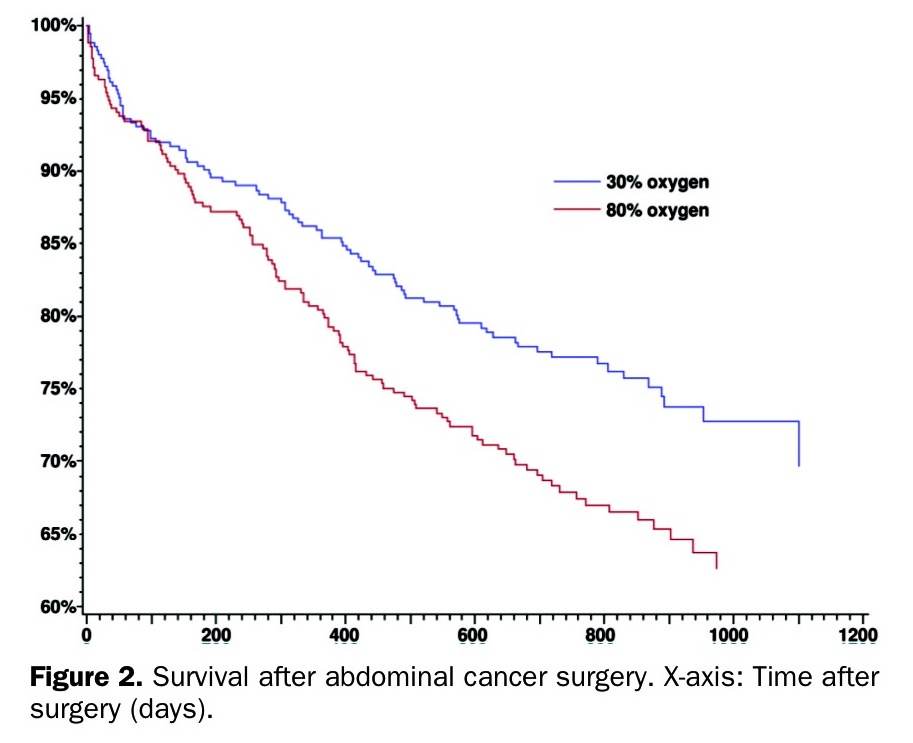
L’article danois qui m’a bien intéressé est une analyse post-hoc d’un essai randomisé de belle amplitude (1400 patients) ayant testé une FiO2 de 80% pour prévenir les infections du site opératoire. Cette étude, le PROXI trial, s’est révélée négative rentrant ainsi en contradiction avec les essais précédents . Par contre les investigateurs ont observé une tendance vers une mortalité augmentée dans le groupe recevant de fortes quantités d’oxygène, ils ont donc réalisé une analyse post-hoc de leur cohorte .
Les résultats montrent une surmortalité dans le groupe recevant de l’oxygène en forte quantité pendant la chirurgie abdominale et en phase de réveil (2h post-op). Ce résultat était plus consistant dans le groupe des patients opérés de cancer. Les auteurs énoncent bien les limites de leur analyse qui ne prouve pas de lien de causalité et ils rapportent bien que les hypothèses physiopathologiques sont peu évidentes. D’autant moins évidentes que la surmortalité ne semble pas s’expliquer par des événements post-opératoires immédiats comme des atélectasies et des détresses respiratoires imputables à l’oxygènothérapie à haut débit. Toujours est-il que ce type d’étude me frappe parce qu’à force de banaliser l’oxygène on oublie que c’est un médicament comme un autre. Je pense qu’il est vraiment important que nous fassions des choix thérapeutiques actifs pour tout ce que nous faisons au patient, y compris pour le réglage de la FiO2 en peroperatoire.
Le deuxième article est une revue de la littérature qui construit un plaidoyer pour une titration plus fine des besoins en oxygène pour les patients les plus graves. Les auteurs démontrent leur propos en s’appuyant sur des études physiologiques démontrant une adaptation possible de l’homme à l’hypoxie et surtout en rapportant des essais ayant démontré que l’oxygène pouvait être péjoratif comme a la phase aiguë de l’infarctus du myocarde . J’ai notamment appris avec ces deux lectures que l’augmentation de la PaO2 déclenchait une vasoconstriction coronaire . Les auteurs reprennent également une partie de la littérature sur le syndrome de détresse respiratoire aiguë (SDRA) en soulignant que les patients meurent rarement (jamais ?) d’une hypoxémie réfractaire mais plutôt de défaillance multiviscérale liée à la pathologie de départ. Ainsi les auteurs cherchent à nous faire réfléchir sur la titration précise de l’oxygènothérapie. Le but de leur revue de la littérature est de nous démontrer que s’il existe des cas où l’hyperoxémie peut-être délétère, il existe peut-être des patients dont le pronostic serait meilleur si nous tolérions ce qu’ils appellent « permissive hypoxemia »
Bref, ces deux articles sont vraiment intéressants. Je pense qu’ils vont influer sur ma pratique clinique. Je conseille vivement ces lectures pour tous les médecins qui pratiquent des soins aigüs.
J’ajoute a posteriori cette illustration issu du blog de Rhazelovitch :
Update novembre 2014 , l’étude AVOID va bientôt paraitre ! cf Scancrit
Update Juin 2016 : un groupe a regardé a posteriori ce que devenaient les patients de deux autres études sur la prévention des infections de paroi où 80% de FiO2 était comparée à 30%. Le résultat est qu’il n’y a pas de différence dans la mortalité. Pour moi, ça ne change pas mon idée qu’il est inutile de donner plus d’oxygène que nécessaire pour une SpO2 normale. Et içi un article de réa intéressant sur hyperoxémie et pneumonie acquise sous ventilation.
12 réponses sur « L’oxygène est un médicament comme les autres ! »
Super topo.
Ce fut un des premiers « take home message » que m’avait donné mon chef de service lors de mon deuxième stage en réa en tant qu’externe.
Le mieux est l’ennemi du bien, y compris et surtout dans l’oxygénothérapie.
Il nous expliquait que l’oxygène sur-dosé entraînait une augmentation de la pO2, vu que l’hémoglobine est, par définition, saturable. Cette hyperoxie serait responsable…. d’un dépassement des capacités des systèmes physiologiques anti-oxydants, avec tout le tintouin des ions superoxydes et des radicaux libres. Et la première victime serait l’alvéole pulmonaire.
Il s’appuyait entre autres sur une étude sur volontaires sains, chez qui on faisait un LBA avant et après 40 minutes d’oxygénothérapie à Fi02=0,4. Sur le deuxième LBA, il y avait un afflux de leucocytes et de cytokines, révélant un état inflammatoire, de composition similaire à ce que l’on voit dans les fibroses pulmonaires.
Pour en revenir au SDRA, la particularité est que cohabitent des alvéoles mortes et collabées, des alvéoles atteintes mais « sauvables » et des alvéoles saines. De la même manière que la ventilation « protectrice » vise à ne pas sur-distendre les alvéoles saines, on peut raisonnablement penser que des FiO2 démesurées puissent être particulièrement toxiques sur les alvéoles saines.
Tout ceci est sans parler des patients insuffisants respiratoires chroniques qui passent d’un trigger « capnie » à un trigger « oxygène » en ce qui concerne leur dynamique ventilatoire.
En conclusion, la règle dans le service est de viser une saturation entre 88 et 95%, y compris et surtout dans le SDRA (certains auteurs iraient même jusqu’à dire que 82% suffiraient), sauf chez le neuroagressé où on vise plutôt 94-98%.
Sources : de mémoire je ne citerai que Réanimation Médicale, chez Masson, le collège national pour le troisième cycle. Il faut que je lui demande les références des articles sur lesquels il se base.
le neuroagressé comme tu dis constitue peut-être une classe à part mais je n’en suis pas persuadé, Daniel Martin cite des exemples dans ce sens
Salut
quelles sont les causes de décès qui expliquent la surmortalite dans le groupe hyperO2, surtout chez les patients cancéreux ?
Une hypothèse est que la progression de la maladie pourrait être favorisée par la presence de l oxygène, même si la durée de l hyperoxemie semble courte.
Oui les auteurs penchent pour une action néfaste de l’oxygène in vivo sur les cellules cancéreuses (stimulation de la néovascularisation par exemple) mais ils disent aussi que c’est en contradiction avec les études in vitro. Bref on ne sait pas. Tu peux accéder sur le PDF de l’article en cliquant sur « L’article danois qui m’a bien intéressé » ça pointe vers le PDF et tu pourras voir la discussion.
En a parte, il y a de plus en plus de littérature qui s’intéresse aux effets de l’anesthésie générale sur le pronostic du cancer (influence négative des morphiniques par exemple, tu peux alelr voir ce billet : http://www.nfkb0.com/2012/01/07/ils-sont-forts-ces-belges/ ) on a du pain sur la planche
Merci d’être passé par ici, à bientôt j’espère
On ne finira pas de brûler les vaux d’or …. Mais pourquoi ? Dans les années 80 on avait largement étudié la toxicité de l’oxygène. Pour finir, l’oxygène semble un peu moins toxique dans la vraie vie que dans les éprouvettes. Bon. Le malade en bonne santé qui perfuse « normalement » ces tissus ne souffre pas, je pense, de cette toxicité. Par contre, le malade qui a une zone en dette ne résiste pas bien à l’hyperoxie. Vu qu’en réa on soigne essentiellement des patients qui ont ce genre de soucis, on comprend pourquoi ne pas y aller large main avec cet oxygène. Par contre, pour l’opéré, on moins de soucis à ce faire. Je pense que cette nuance explique en partie les différences vues entre les opérés et les patients de réa.
Enfin, pour les infections de paroi, il me semble que l’étude danoise ne prend pas assez en compte la notion de fenêtre d’opportunité. Certaines équipes sont tellement soigneuses sur ce qui compte le plus : température, durée d’intervention, aspepsie, circulation du personnel en salle, antibiothérapie, lavage des mains …. que changer la FiO2 ne …. change rien. À l’autre bout, d’autres équipes négligent tant ce qui est important (parfois en s’accrochant sottement à ce qui est pas démontré utile) que l’O2 ne peux les « sauver ».
Voilà un concept que j’adore par dessus tout : la fenêtre d’opportunité
Salut Didier ! Merci pour ton commentaire.Effectivement il est probable que la FiO2 ne soit pas toxique pour la majorité des patients.
Mais que penser des courbes de survie pour les patients opérés d’un cancer, c’est intrigant tout de même non ?
biz
Souvenez-vous ! Qui pensait il n’y a pas dix ans que les opioïdes large main augmentent le risque de récurrence de cancer ?? Au risque de paraître un peu désuet, la maxime « in medio stat vertus » continue d’être tellement vraie.
[…] subaigu, il faut effectivement se méfier d’une oxygénothérapie inadaptée. L’oxygène est un médicament comme les autres, il y a des indications et une posologie. Il faut toujours savoir et comprendre pourquoi un patient […]
[…] L’oxygène est un médicament comme les autres , NFKB blog […]
[…] subaigu, il faut effectivement se méfier d’une oxygénothérapie inadaptée. L’oxygène est un médicament comme les autres, il y a des indications et une posologie. Il faut toujours savoir et comprendre pourquoi un patient […]
Dans l’infarctus du myocarde, après AVOID (cité dans le blog) vient de paraitre DETOX2 (NEJM 2017) qui montre qu’on peut se passer d’oxygénothérapie si la saturation et supérieure à 90% (!!!). Ce qui a entrainé une correction des recommandations de l’ESC : l’oxygénothérapie systématique n’est pas recommandée si pa SpO2 > ou = à 90% (niveau III de recommandation : il ne faut pas faire)
Idem dans l’AVC, avec l’étude SO2S (JAMA 2017) avec une barre de SpO2 à 93%
L’oxygène est un médicament qui a ses indications, contrindications et posologie
Merci pour la complémentarité de ces informations